Reconstructing the pre-settlement vegetation of the Yellow River watershed and its implications for restoration and land management
- Student
- Caitlin Broderick
- College(s)
- College of Science
- Faculty Advisor
- Jason McLachlan
- Class Year
- 2017
Historically, closed eastern forests transitioned into open savannas and prairies in the US Midwest, but this transition is poorly understood. To investigate the eastern boundary of the prairie-forest ecotone, we conducted a case study of historic and modern vegetation patterns of the Yellow River watershed in northwest Indiana.
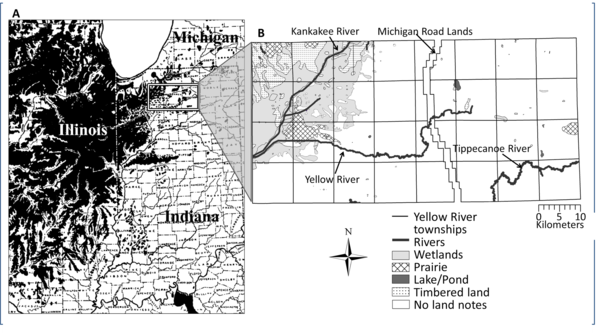 (A) Transeau’s (1935) depiction of the prairie before Euro-American settlement, with study area outlined. (B) Yellow River watershed study area and the digitized surveyor-drawn plat maps of the region.
(A) Transeau’s (1935) depiction of the prairie before Euro-American settlement, with study area outlined. (B) Yellow River watershed study area and the digitized surveyor-drawn plat maps of the region.
Historic vegetation came from the Public Land Survey notes collected in the early 1800s, whereas modern vegetation came from the Forest Inventory Analysis and USGS National Land Cover Database. We mapped historical survey vegetation data using GIS to reconstruct the region’s past and current forest composition and structure. We also mapped climate, topography and soil composition across the watershed to investigate the relationship between historic vegetation and environmental gradients.
We found a sharp transition in the pre-settlement forest structure and composition, with dense deciduous forests in the eastern portion of our study area and open oak savannas in the west. The savanna ecosystem dominated in sandy, well-drained soils and was at a slightly lower elevation than the adjacent closed forest. Modest environmental changes accompanied major vegetation changes in the past, which might suggest that fire and hydrological patterns helped maintain the sharp ecotone. By contrast, the modern forest shows no difference in tree density and composition across the watershed, which is consistent with major land use and hydrology changes in the watershed since settlement. On the modern landscape, land that was historically closed forest now has higher agricultural productivity compared to land that was historically savanna, whereas the historic savanna currently supports more mesic forest.
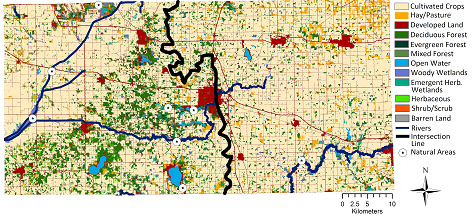 2006 land use of the Yellow River watershed in each historic vegetation area
2006 land use of the Yellow River watershed in each historic vegetation area
These results suggest that the environmental gradient continues to subtly shape the landscape. Though land use change has largely removed the closed mixed hardwood and oak savannas from this area, a better understanding of the historic vegetation and the conditions that supported it can help inform land management and restoration, as well as reveal ecological processes that drive vegetation transitions.